Diagnostic Medical Sonographer vs Radiology Technician
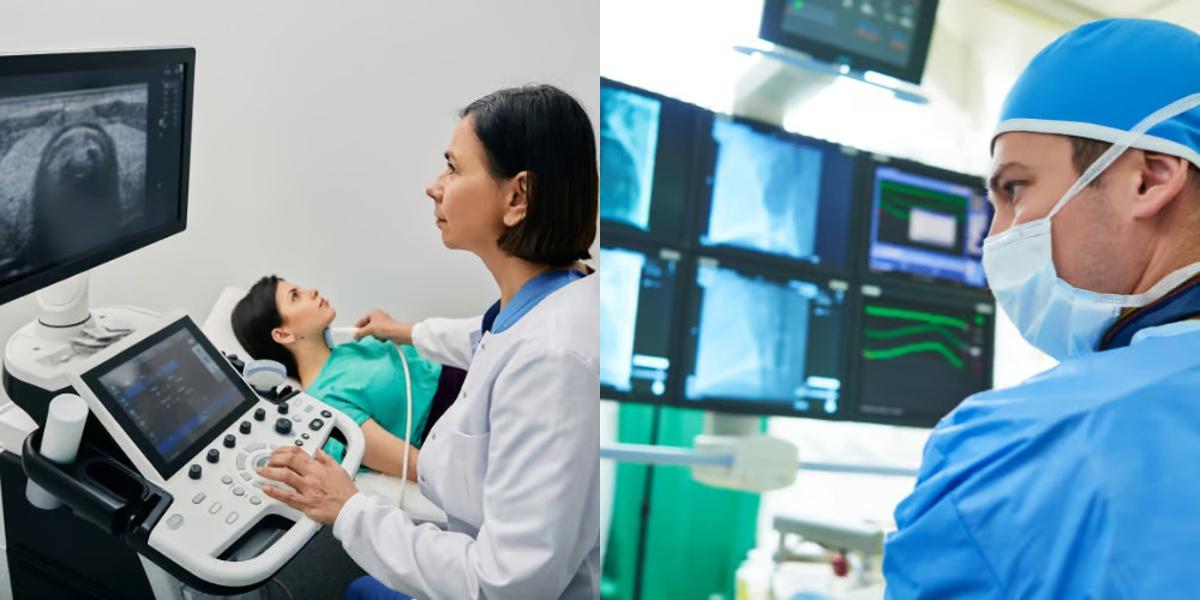
Exploring a career in medical imaging? Many students and career changers ask, “Should I become a Diagnostic Medical Sonographer or a Radiology Technician?” Both are in-demand healthcare careers with strong salaries, but they differ in training, daily work, and long-term opportunities. Sonographers earn a median salary of $89,340 per year, while Radiology Technicians earn $77,660. This guide compares responsibilities, education, pay, and job outlook so you can choose the path that matches your goals.
Salary and Career Outlook
Diagnostic Medical Sonographer
- Median Salary (May 2024): $89,340/year (BLS).
- Job Growth: 15% through 2033, much faster than average (BLS).
- High demand in hospitals, outpatient centers, and OB/GYN practices.
Radiology Technician
- Median Salary (May 2024): $77,660/year (BLS).
- Job Growth: 6% through 2033, faster than average (BLS).
- Demand steady in hospitals, diagnostic labs, and urgent care facilities.
State Licensure: A Closer Look
Licensure requirements are not universal and vary significantly by state and profession. Always check the rules for the state where you plan to work.
- For Radiology Technicians: Many states require a license. In New York, for example, you cannot practice or use the title "radiologic technologist" without a license issued under Article 35 of the Public Health Law. This requires completing an approved program and passing a certification exam.
- For Diagnostic Medical Sonographers: Fewer states mandate licensure, but the number is growing. In New Mexico, sonographers must be licensed by the Medical Imaging and Radiation Therapy Program (MIRTP). Licensure requires graduating from an approved program and earning a national certification, such as from ARDMS.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it harder to become a sonographer or a radiology technician?
- Sonography programs are often considered more intensive due to the high degree of anatomy knowledge and hand-eye coordination required for real-time scanning. However, both fields have rigorous academic and clinical requirements.
How much does training cost?
- Program costs vary widely by school type and location. Associate degree programs for either field generally range from $6,000 to $40,000. Certificate programs may cost less.
Which career is better for patient interaction?
- Sonographers typically spend more one-on-one time with patients, as ultrasound exams are dynamic and can last from 20 minutes to over an hour. Radiology technicians have shorter, more procedural interactions focused on positioning the patient for a scan.
Final Thoughts
Both careers offer stability, competitive pay, and the opportunity to make a difference in healthcare. The right choice depends on your personal and professional preferences.
If you enjoy specialized, hands-on work with ultrasound technology and value extended patient interaction, becoming a Diagnostic Medical Sonographer may be the right fit.
If you prefer working with a variety of imaging technologies and have a strong aptitude for technical procedures and safety protocols, a career as a Radiology Technician could be your ideal path.
Dreambound makes it easier to start your career in medical imaging. Explore accredited training programs in your area today:

Pia Yapjoco is part of the school growth and sales team at Dreambound. She helps facilitate school partnerships that expand educational opportunities for aspiring students in allied health and other trades. Beyond work, she curates her pup's Instagram, hunts for hidden coffee gems, and escapes into cozy gaming.



